Deep Dive into Data Analyst Career Roles
29 May 2024
Introduction
Have you ever wondered how Instagram shows you the exact reels that you have been talking about to your friends?
How does Google know exactly what your next purchase is going to be and you see similar ads everywhere?
How does Netflix display your next watch before you even think about it?
They can do this because they take these insights from YOU. Yes, you give away a lot just by watching a series on Netflix or by scrolling through reels on Instagram.
“What is this Sorcery” you may ask. This is all possible with the help of Data and Data Experts.
Data Analysts are like Astrologers in the digital world, predicting your next moves through the data traces left behind by you. Sounds interesting right? Let’s know more about the types of data wizards that do this.
Data Analysts can enter a variety of long-term career roles. Broadly these career roles can be divided into Technical and Non Technical.
Non-Technical Career Path
This career path usually does not have any strict background requirements and is purely based on acquired skills. A candidate who wants a career in this field is required to possess the following skills-
Data Handling and Visualisation skills
Problem-solving skills
Analytical skills
Management skills
Communication skills
Domain Knowledge
A Non-Technical Data Analyst career can branch into any type of sector like finance, marketing, sales, etc. The most popular career roles are in this field-
Business Analyst
A Business Analyst is a very generalist kind of role where the analyst is required to carry out a variety of tasks, varying from case to case ranging from optimising business processes to project management to carrying out stakeholder communications. Anything that improves the business offerings and involves stakeholders' direct interest can be a business analyst’s task.
Financial Analyst
Financial Analysts are responsible for developing financial models, developing budgets, conducting variance analysis, forecasting to predict the company’s performance, etc. Their main focus is on financial planning and assessment of the financial health of the company. These require in-depth domain knowledge and often extra professional degrees in the field are preferred. However, if the candidate possesses sound domain knowledge as well as decent skills in data analysis tools, then the degrees do not matter in this field.
Market Research Analyst
Market research analysts are responsible for conducting surveys, interviews, competitor analysis, collecting feedback, assessing the markets, etc. In broader terms, they collect, evaluate, analyse and communicate the company’s product position from external data sources. It is an essential role, especially in new companies in the developing stage as it helps the company serve their niche customers better, and in many cases the best. Rolling out Instagram Reels after the ban of the popular application “Tik-Tok” in India was a result of active market research and quick action when given an opportunity by Instagram, resulting in its product becoming a major amongst its customers.
Social Media Analyst
A social media analyst is responsible for user data collection and analysis, development of content strategies, providing audience insights, campaign strategy and insights, etc.
Since social media has become very prevalent in the current days, this is a very up-and-coming career path. Social media influencers or businesses marketing their products on social media, all follow very different strategies to attract their customers on their respective platforms. Hence, an analyst is required to have in-depth knowledge of their client’s offerings, their niche customers and their expectations.
Technical Career Path
Technical career paths require strong hard skills like programming, theoretical knowledge and applicative knowledge of the respective tools used by each of them. Popular job roles in this career path are Data Scientist, Data Engineer and Quantitative Analyst. Even though a relevant educational background is not always necessary for these kinds of roles, it is always highly preferred over a non-technical one. Also, sufficient work experience in the related field is highly valuable (sufficient varies from situation to situation).
Data Scientist
Data Scientists, also often referred to as Machine Learning Experts, are responsible for analysing and interpreting complex business data to develop predictive models for establishing trend patterns and decision-making. Their work involves the next step of the work that a Data Analyst does. Their models use statistical knowledge and machine learning skills, hence a background in Statistics or Computer Science is preferred in these job roles.
Data Engineer
Data Engineers are responsible for developing the data pipelines and managing the databases. They handle the process of data management and cleaning before data analysts and scientists do. In fact, the stronger the data pipeline built by data engineers, the easier it is to access data for the data analysts and scientists. Thus data engineers require fortified skills in database management tools like MongoDB and PostgreSQL as well as robust knowledge of software engineering.
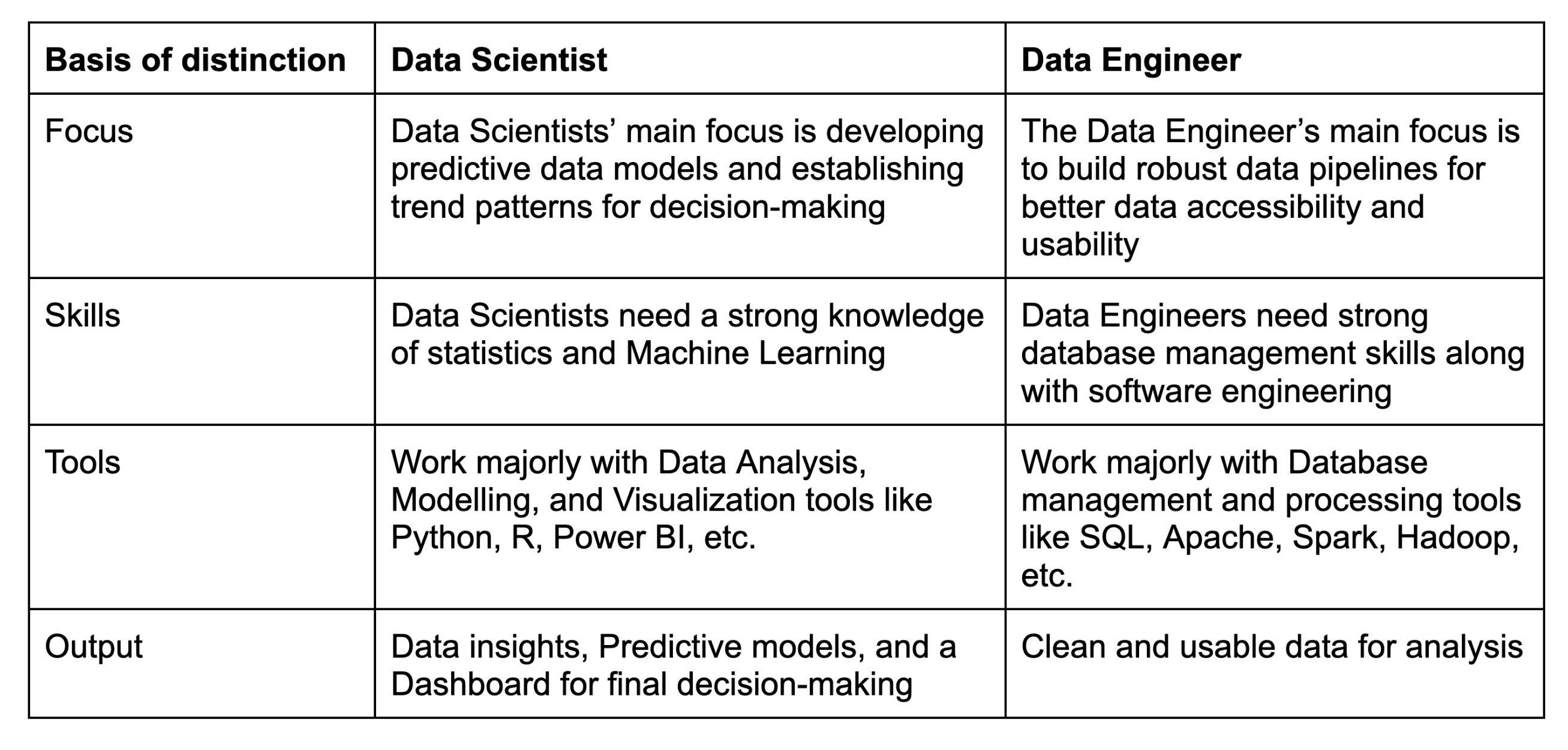
Data Engineers are often confused with data scientists and are sometimes even thought to be the same! However, even though tier work is complementary, it is not the same. They play very distinct and important roles in any organisation. Let’s understand how their roles differ from each other from the below table-
Quantitative Analyst
A lot of us trade in the stock markets and buy and sell stocks, bonds and other instruments on a daily. However, the majority of us lack proper knowledge and trading for us is like betting, a pure game of luck. Quantitative analysts are the people who quantify this process and trading is not a betting game who them. Quantitative Analysts mainly work in trading, risk management and investment strategies roles. Their main role is to develop mathematical models to identify, analyse and capitalise on financial opportunities. They require advanced mathematical, financial and statistical knowledge as well as programming skills in Python, C++, R or MATLAB. It is a highly technical role and requires a strong background in maths/ stats as well as several years of work experience in the relevant field.
Conclusion
Data Analyst roles are of various types and can be taken up by anyone, irrespective of their previous backgrounds. However, it is more viable to get into the non-technical roles first and then progress to the technical roles, since the technical roles require strong domain knowledge and hard skills. These skills can be developed while working in non-technical roles, which are beginner-friendly and are comparatively less skill-intensive. Also, these career paths offer high growth prospects and steep learning curves, hence making it a very lucrative career path. So are you ready to enter this world of wizardry?